Most of the time, you probably don’t think too much about your bladder.
Until you need to empty it, that is, and then it’s all you can think about.
Especially if you don’t have easy access to a toilet.
But not needing to urinate at all – or conversely needing to do it too much – can be a sign of health issues.
If you’re worried about this, then you may be thinking “I need to find a nurse practitioner clinic” to find out what’s wrong.
Keep reading to find out more about your bladder, the health conditions that can affect it, and some tips for keeping it healthy.
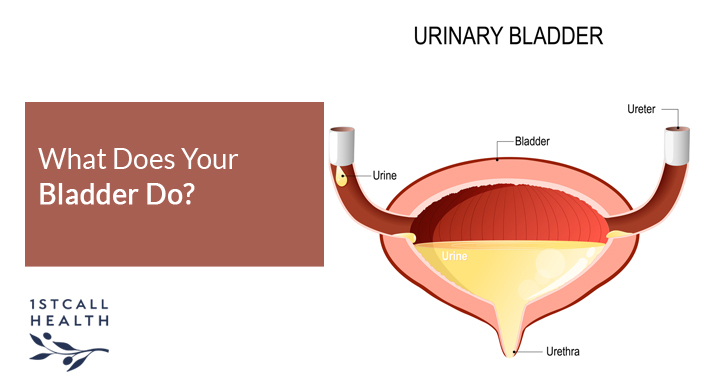
What Is Your Bladder?
Your bladder is a hollow, triangular shaped muscular sac located in the lower portion of the abdomen, behind the pelvis.
Its walls enlarge and relax to store urine, and then contract to empty it.
In the average healthy adult, your bladder should be able to store about two cups of urine for up to five hours.
What Are The Functions Of The Bladder?
The function of the bladder is to store your urine until you’re ready to urinate.
Imagine if you didn’t have the ability to store fluid for any amount of time.
You’d need to rush to the bathroom every time you wanted to have something to drink.
This would be pretty inconvenient and demonstrates why it’s important to keep your bladder healthy.
Common Bladder Disorders
In this section, we’ll take a look at some of the common issues that can affect your bladder and how to recognize them.
1. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
When you urinate, urine empties out of your bladder and out of your body.
It does this via your urethra, a tube connecting your bladder with the outside of your body.
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria gets into your urethra, resulting in an infection of the urinary tract.
Types of urinary tract infections include bladder infections and kidney infections.
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection include:
- Frequent urination
- Painful urination
- Blood in your urine
- Abdominal cramps
It’s important to get treatment for UTIs.
They’re fairly easy to treat, but if left untreated they can cause bigger health issues.
2. Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is also known as a loss of bladder control.
It can be range from minor to severe.
Minor incontinence could be a little bit of urine leaking when you laugh or cough.
Severe incontinence might look like a sudden and strong need to urinate, without time for you to reach a toilet.
There are a few different types of incontinence.
It’s also possible to experience more than one type of incontinence at the same time.
These include:
Functional Incontinence
Functional incontinence is caused by an impairment that prevents you from making it to the toilet on time.
Urge Incontinence
Urge incontinence is the unexpected need to urinate, alongside an automatic loss of urine.
This is sometimes caused by another underlying condition.
Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence is the most common type of urinary incontinence.
It’s caused by force applied on your bladder.
This can include laughing, sneezing, or coughing.
If you’ve been pregnant, are postmenopausal, or have a family history, you may be at greater risk for stress incontinence.
Overflow Incontinence
Overflow incontinence is when your bladder doesn’t empty completely, resulting in dripping or a leak
3. Enlarged Prostate
If you have a prostate, it’s common for it to grow in size as you get older
This can make urination difficult.
As well, many of the symptoms of an enlarged prostate are linked to the bladder and urination.
These include:
- Incontinence
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
- Leaking or dribbling after peeing
- Dysuria (pain while urinating)
- Hematuria (blood in the urine)
- Urinating multiple times during the night
Treatment for an enlarged prostate will depend on the severity of symptoms and can include lifestyle changes, medications, or even surgery.
4. Urinary Retention
Just as its name suggests, urinary retention is when your bladder doesn’t empty completely, resulting in retaining urine.
It’s a condition linked to health issues related to the prostate or muscles which support your bladder and vaginal wall.
How To Keep Your Bladder Healthy
Bladder issues aren’t a lot of fun.
But the good news is there are plenty of things you can do to reduce your risk and keep your bladder healthy.
Here are some of our key tips for maintaining bladder health.
1. Stay Hydrated!
Your body is about sixty percent water, which means it works best when it’s properly hydrated.
If you’re urinating every few hours, you’re probably getting enough hydration.
Certain medical conditions might mean it’s best to drink more or less than this amount though.
For example, if you’re diabetic, it’s a good idea to drink more than the average amount of water.
This is because drinking water can help flush out excess glucose.
If that’s the case for you, your 1stCallHealth primary care provider will discuss this with you in more detail.
Make sure to stick with water, decaffeinated coffee/teas, and other drinks that don’t have too much sugar.
Among other issues, sugary drinks can actually dehydrate you, keeping you thirsty.

2. Eat A Bladder Friendly Diet
Issues with your bladder can often be linked to things in your diet.
Certain types of food can often worsen already existing bladder issues.
These may include:
- Tomatoes
- Artificial sweeteners
- Soda or other sugary drinks
- Spicy foods
- Citrus fruit
If you are experiencing bladder issues, try eliminating the foods listed above.
3. Avoid Drinking Too Much Coffee
Coffee and other drinks containing caffeine (like tea, and soda) are diuretics.
This means they increase the production of urine.
As a result, coffee may increase symptoms which can cause urinary issues, and increase the urgency and frequency of urination.
4. Avoid Holding Your Urine For Too Long
Simply put, if you have to go, then go.
As already noted, you should be drinking enough fluids so you’re peeing every few hours.
Holding your urine for too long can lead to weakened bladder muscles and increases your odds of developing an infection.
If you know you have incontinence, it can help to schedule times to use the washroom.
5. Empty Your Bladder When Urinating
If you don’t take the time to fully empty your bladder when you urinate, it can lead to issues.
Infections are more likely if urine stays in the bladder for too long.
Be sure to relax your muscles and take enough time to allow your bladder to empty fully.
Book Your Appointment With 1stCallHealth Today
Are you worried about the health of your bladder?
Or maybe you have other health concerns you’d like to address.
We’re 1stCallHealth, and our goal is to help everyone access affordable, high quality primary care services.
Book your appointment with 1stCallHealth today.
1stCallHEALTH
1331 H St NW Ste 200,
Washington, DC 20005
(202) 590-0009
– https://goo.gl/maps/MVhjkz2jqynWpsgo6
1stCallHEALTH provides affordable access to primary care services. We believe that everyone deserves affordable, high quality primary care. Our vision is to challenge the status quo, focus on the individual, and empower personal control to change the way we think about healthcare.




